In 2017, the world witnessed an unparalleled financial phenomenon: the ICO (Initial Coin Offering) boom, where blockchain projects raised billions of dollars in mere minutes.
While many saw this as a speculative bubble, a deeper trend was emerging, driven by a foundational technology: smart contracts on platforms like Ethereum. These contracts gave birth to a new financial paradigm, Decentralized Finance (DeFi).

With DeFi, we're not just seeing a shift in how funds are raised, but a seismic movement towards a democratized financial system. Bypassing traditional gatekeepers, from banks in New York to microfinance in Nairobi, DeFi has the potential to place financial control back into the hands of individuals, transcending borders and socio-economic statuses.
This isn't a distant future; it's a transformative present, and to understand its magnitude, we must dive deep into DeFi's intricacies, promises, and challenges. Get on this interesting journey with Global Blockchain Solution in today’s blog.
This Article Contains:
Background and Historical Context
The 2008 financial crisis, triggered by the fall of Lehman Brothers and reverberating across global economies, exposed deep vulnerabilities in the centralized financial systems. As trust in banks eroded, a mysterious entity named Satoshi Nakamoto introduced Bitcoin, a decentralized digital currency, to the world.
This wasn't just a new kind of money; it was a bold critique of traditional finance, championing decentralization over centralized control. But Bitcoin was just the beginning.
Fast forward to 2015, Ethereum entered the scene. Unlike Bitcoin, which was primarily a digital currency, Ethereum introduced a more versatile tool: smart contracts. These self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code lines expanded the horizon of what was possible on blockchain technology.
Also Read: What are Smart Contracts?
Now, beyond simple transactions, complex financial applications can be built and executed without intermediaries. This was the true genesis of DeFi. Traditional financial instruments - from loans to insurance, from exchanges to asset management - began finding their decentralized counterparts on Ethereum's platform.
The world was waking up to the possibilities: what if everyone, regardless of their location or economic status, could access financial services without traditional gatekeepers? This vision underpins DeFi's rise and the broader transition from centralized trust in institutions to decentralized trust in code and consensus.
Core Principles of DeFi
At the crux of DeFi's evolution are guiding principles that not only redefine our understanding of finance but lay the groundwork for a more inclusive global financial system.
Decentralization
Historically, centralized exchanges (CEX) like NASDAQ and NYSE have dominated stock trading. According to NASDAQTrader.com, NASDAQ issues are traded over $200 billion in daily volume. However, this trading is facilitated through intermediaries and centralized entities, leading to potential points of failure, slower transactions, and possible fee variances compared to some decentralized platforms, along with a lack of transparency in some cases.
Enter DEXs like Uniswap, which, as of Q3 2023, had overseen over $489 billion in trades and over a billion in daily volume. With no central point of control (and failure), DEXs utilize automated market makers (AMMs) to facilitate trades. This democratizes the process and reduces the risks of centralized control, although users might sometimes face high costs during times of network congestion.
-
Transparency
Traditional banks and financial institutions often operate behind closed doors. For instance, during the 2008 financial crisis, obscured debt obligations and derivatives played a part in the global meltdown.
DeFi, however, champions transparency. Platforms like Etherscan allow users to openly view and verify transactions on the Ethereum blockchain. This means every DeFi transaction, be it on Aave or Compound, is auditable by the public, reducing the chances of hidden financial malfeasance.
-
Permissionlessness
Creditworthiness in traditional finance is often a roadblock. According to the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), approximately 26 million U.S. adults are “credit invisible” as they lack a credit record. This is despite the U.S. being a capitalist market. The situation gets a lot murkier across developing economies.

DeFi operates differently. Platforms like MakerDAO allow users to take out loans by over-collateralizing with assets, effectively sidestepping the need for credit checks. Furthermore, platforms like dYdX and Sushiswap offer powerful decentralized trading options and flash loans, allowing users to access large sums of capital quickly without collateral.
This approach broadens financial access, especially for those sidelined by traditional credit systems.
-
Interoperability
In the legacy financial system, integration between services is cumbersome. For instance, even with advancements in fintech, transferring funds from PayPal to a bank account might take a day – and up to 3-5 business days.
DeFi operates on a shared infrastructure, primarily the Ethereum blockchain. This means a user could take out a loan on Aave, immediately use that loan to provide liquidity on Curve, and then stake the resulting liquidity tokens on another platform, all in a matter of minutes.
This composability is often referred to as "money legos" in the DeFi community, emphasizing the ease of integrating various DeFi protocols.
By rooting itself in these principles and showcasing tangible, real-world applications, DeFi presents a compelling case for the future of finance — one that's not just technologically advanced, but also more aligned with the needs of its users.
What Are Different Types of DeFi Platforms?
As we peel back the layers of DeFi, its potential begins to shimmer with clarity. It's not just about remaking existing financial systems but pioneering new ways to interact with money and assets. Here are some standout applications and the innovations they bring:
-
Yield Farming and Liquidity Mining
Once, the idea of earning interest on your assets was limited to bank savings accounts with minuscule returns. DeFi's yield farming upends this, offering more attractive returns to those providing liquidity.
Platforms like Yearn Finance automate yield farming strategies to maximize returns. In 2023, data from DeFi Pulse indicated that $95.28 billion were locked in DeFi protocols such as yield farming, a testament to its allure.
Also Read: What is Consensus Mechanism in Blockchain? 25 Consensus Mechanisms to Choose From
-
Decentralized Stablecoins
While cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum hold transformative potential, their volatility can be a deterrent. Enter decentralized stablecoins like Dai, pegged to the US Dollar and minted through collateralization on platforms like MakerDAO.
Unlike centralized counterparts, which are backed by actual fiat in bank accounts, decentralized stablecoins like DAI derive their stability through over-collateralization with other cryptocurrencies, providing a more trust-minimized and transparent approach.
-
Decentralized Insurance
Traditional insurance companies can be laden with bureaucracy and often suffer from a lack of transparency. DeFi introduces decentralized alternatives like Nexus Mutual, where users can get coverage against smart contract failures.
Through Nexus Mutual, members can buy coverage, stake, and claim in a peer-to-peer manner, reducing the need for intermediaries and providing a more direct and transparent insurance process.
-
Tokenized Assets
Imagine owning a fraction of a Picasso painting or a vintage sports car. Traditionally, ownership of such high-value assets was beyond the reach of most.
DeFi's tokenization potential enables the division of such assets into smaller, tradable units. Platforms like Nyala break down physical assets into blockchain tokens, democratizing access and enabling a wider pool of investors to own and trade fractions of these assets.
-
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
Beyond finance, DeFi principles are reshaping organizational structures. DAOs, like the famed Compound or the grant-dispensing Gitcoin, are community-led, transparent organizations on the blockchain. With built-in governance tokens, every token holder can have a say in the direction of the organization, making decisions more decentralized and democratic.

The above are just glimpses into the vast landscape of DeFi's potential. The underlying ethos remains the same: decentralization, democratization, and transparency. As DeFi continues to mature, it promises to unlock even more innovative financial products and services, challenging and potentially surpassing their traditional counterparts.
Advantages of DeFi: A Real-World Perspective
DeFi's transformative power is evident through tangible developments and statistics in the real world.
Let's delve deeper into the distinct advantages using real-world examples and insights:
-
Accessibility and Financial Inclusion
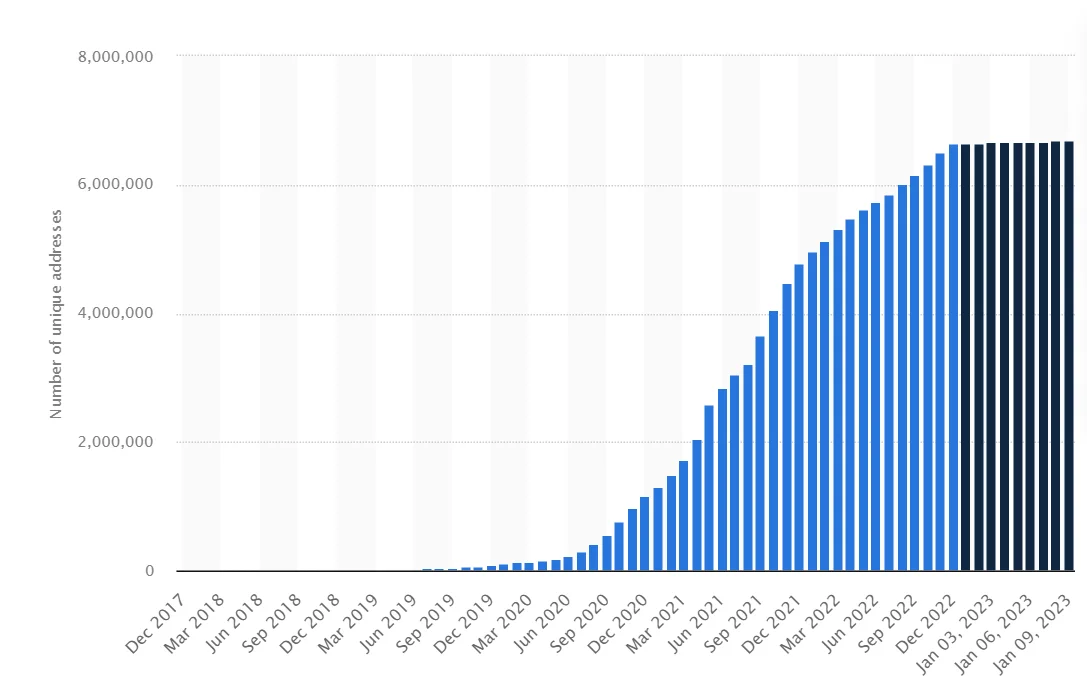
Consider the surge of DeFi users from a mere 189 in December 2017 to over 6.6 million by January 2023, as reported by Statista. This growth exemplifies DeFi's reach across various demographics.
Take the example of Centrifuge, which enables real-world assets like invoices or real estate to be used as collateral, bridging traditional finance and DeFi.
-
Streamlined Operations with Fewer Intermediaries
Uniswap, a decentralized exchange, has shown how liquidity provision can be democratized. Traditional exchanges relied on market makers for liquidity, but platforms like Uniswap have streamlined this with automated market makers (AMMs), leading to $489 billion in trades since its launch in 2018.
-
Empowerment through Asset Control
Platforms like Argent are perfecting the balance between user autonomy and security. Argent offers a non-custodial wallet but includes safeguards like daily transfer limits and wallet locking, showcasing DeFi's evolving user-centric approach.
-
Transparency and Open-Source Auditability
Compound, a leading DeFi lending protocol, showcases this by putting its governance and system functions on-chain, allowing for unparalleled transparency and community-driven decisions. This model ensures accountability, with over $2.5 billion in assets earning interest transparently.
-
Innovation and Composability
The rise of Yearn Finance exemplifies DeFi's innovation. Orchestrating various platforms to maximize yield, it's a testament to how DeFi protocols can interoperate, leading to efficient and innovative financial strategies.

-
Global and Borderless Operations
Aave's deployment across multiple networks, including Ethereum and Polygon, underpins DeFi's global and borderless nature. Their global footprint ensures users from different regions can access services with ease, marking a departure from geographically constrained traditional financial services.
-
Programmability and Customization
Synthetix's rise in the DeFi space underscores the power of programmability. By allowing anyone to mint and trade a vast array of synthetic assets, from cryptocurrencies to commodities like gold and oil, Synthetix provides a platform where traditional and digital finance can converge.
-
Potential Market Efficiency
Balancer's automated portfolio management showcases market efficiency in DeFi. By automatically rebalancing weights, Balancer ensures liquidity providers get optimal returns. This dynamic approach contrasts with the static nature of traditional financial instruments, pushing the boundaries of market efficiency.
Infused with real-world applications and driven by dynamic developments, DeFi's advantages promise a future where financial systems are more inclusive, transparent, and user-oriented. With every real-world implementation, DeFi's potential to revolutionize the financial landscape becomes more tangible.
The Next Frontier And The Challenges To Overcome
The DeFi landscape is teeming with promise, poised to reshape global finance in unprecedented ways. As this ecosystem journeys into uncharted territories, it reveals breathtaking vistas of potential and encounters formidable challenges.
-
Layer 2 Solutions and Scalability
The rise of Layer 2 solutions, like Optimistic Rollups and zk-Rollups from projects such as zkSync and Optimism, addresses DeFi's need for scalability by enhancing transaction speeds and reducing costs.
Also Read: Blockchain Scalability in High-Throughput Applications
However, the very novelty of these solutions means they sometimes grapple with security vulnerabilities, making the protection of user funds a top priority.
-
Cross-Chain Interoperability
Seamless communication between blockchains is no longer a distant dream, thanks to initiatives by Cosmos and Polkadot. This breakthrough could effectively erase barriers between diverse blockchain ecosystems.
Yet, achieving true interoperability isn't just a technical challenge. It necessitates consensus among different projects, and history shows that such coordination can be elusive.
-
Advanced Financial Products
DeFi is not resting on its laurels. Platforms like Ribbon Finance are innovating and introducing complex financial products tailored to a wide array of investor needs. But with complexity comes the challenge of clarity. Ensuring users fully grasp these intricate products will be crucial to prevent unintended financial setbacks.
-
Decentralized Identity and Privacy
Balancing blockchain's inherent transparency with user privacy is the next frontier, with projects like Iden3 leading the charge. This delicate balance, however, will constantly be tested by regulatory concerns, making the integration of decentralized identity solutions a complex endeavor.
-
Mainstream Integration and Partnerships
The integration of DeFi into mainstream finance is more a question of 'when' than 'if', especially with major players like Visa exploring USDC integrations and Fidelity Investments delving into crypto. The convergence of traditional finance and DeFi's decentralized spirit, though, will necessitate innovative legal and operational frameworks.
-
Governance and Community Involvement
The potential of DAOs in driving robust, community-led governance structures in DeFi is immense. However, the democratic ethos of DAOs also presents a challenge: ensuring decisions are both representative and efficient and preventing undue concentration of power in a decentralized environment.
-
Security Enhancements
The need for robust security in DeFi cannot be overstated, and platforms specializing in smart contract audits, like ChainSafe, are becoming indispensable. However, as DeFi platforms proliferate and diversify, establishing and maintaining a consistent security benchmark will be a Herculean task.
-
Education and Awareness
The role of educational platforms such as 101 Blockchains and EthHub in driving mainstream adoption is crucial. This education and awareness should transcend any hype around the industry, being grounded in the veritable truths and near possibilities.
As DeFi charts its path forward, its success will hinge on the ecosystem's ability to leverage its strengths while addressing its challenges head-on, keeping its revolutionary promise alive.
At Global Blockchain Solution, we are passionate about everything related to blockchain. If you have any questions or need assistance while developing your DeFi solution, feel free to contact us or get a free 15-minute consultation.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is DeFi and how it works?
DeFi or Decentralized Finance refers to financial applications built on blockchain networks, primarily Ethereum. It aims to provide financial services like lending, trading, insurance, etc without any central intermediaries.
DeFi applications are built using smart contracts which are self-executing codes on the blockchain. For example, a lending platform may have a smart contract that autonomously facilitates lending and borrowing based on collateral provided by users. The terms are transparently coded into the smart contract.
Users interact directly with these DeFi applications through wallet apps like MetaMask. Transactions are recorded transparently on the blockchain. This eliminates centralized control and the need for traditional financial intermediaries.
2. What is DeFi in crypto?
DeFi stands for Decentralized Finance and refers to financial applications in the crypto space that operate without central intermediaries. Instead, DeFi applications use smart contracts on blockchains like Ethereum to offer financial services.
Some examples of popular DeFi applications in crypto are:
MakerDAO - A lending platform to take out loans by providing crypto as collateral.
Uniswap - A decentralized exchange to trade crypto tokens.
Compound - A lending and borrowing platform where users earn interest on supplied assets.
Aave - An open-source lending protocol to earn interest on deposits and borrow assets.
So, in essence, DeFi aims to recreate traditional financial systems in a decentralized architecture, leveraging the transparency and security of blockchain technology.
3. What is DeFi used for?
Here are some of the main use cases of DeFi:
Borrowing and lending - Platforms like Aave and Compound allow peer-to-peer lending/borrowing without intermediaries.
Trading & Investing - Decentralized exchanges like Uniswap and Curve allow the trading of crypto assets without centralized entities.
Earning interest - By supplying assets to DeFi protocols, users can earn attractive interest rates through yield farming.
Derivatives - Platforms like Synthetix enable the creation and trading of synthetic assets and derivatives.
Insurance - DeFi insurance projects like Nexus Mutual offer coverage against smart contract risks.
Payments - Stablecoin payment projects like Celo integrate DeFi with payment solutions.
Asset tokenization - DeFi enables fractional ownership of assets like real estate through tokenization.
So, in summary, DeFi aims to build an open, transparent, and decentralized financial system using blockchain technology.






Comments
Share Your Feedback
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *